What is cop of heat pump?
In an era where energy efficiency and environmental sustainability are paramount concerns, air source heat pumps and also geothermal heat pumps have become a remarkable technology for heating and cooling applications. They offer a way to harness renewable energy sources and minimize the carbon footprint of residential and commercial buildings. At the heart of a heat pump’s efficiency is a critical metric known as the heat pump coefficient of performance (COP). This article delves deeper into the concept of COP, what it means, and how it affects heat pump performance. If you have question about best COP heat pump or typical COP of heat pump, this post is for you! This article is best to be read after reading the article on basic heat pump operation.
Definition of cop heat pump
Now, what is the heat pump COP formula? You already know that it is crucial in terms of heat pump efficiency for your home.
The coefficient of performance, or COP, is used to evaluate the efficiency of a heat pump system. This is the amount of heating or cooling produced per unit of energy consumed. COP is usually expressed as a dimensionless number or ratio, and it is calculated using the formula: In this equation, “heating or cooling provided to the home” refers to the heat or cooling provided to the conditioned space, while “electrical energy consumed” represents the source of electrical energy required to operate the heat pump. The amount of energy exchanged in the evaporator coil is indicated by QH in the image below which shows a heat pump in heating cycle. The input electrical energy (which is paid for) is W. Both QH and W must be in the same unit of power like Watts, BTU/h. Therefore, COP is QH/W. It is important to note that COP is the ratio of QH to W at any given time. It would be interesting to know an average of QH and W over the entire season. This brings us to the definition of the Heating Seasonal Performance factor (HSPF) for winter.
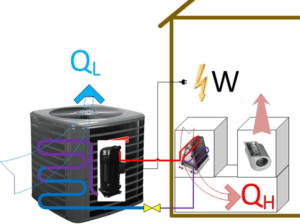
Figure 1- A heat pump in a heating cycle (The evaporator or indoor coil distributes heat, QH, to the circulating indoor air)
Understanding the Importance of cop
The Coefficient of Performance (COP) is a crucial metric for understanding how efficiently a heat pump operates. Put simply, a higher COP means your heat pump turns more of its energy input into useful heat or cooling. A lower COP means it wastes more electricity to do the same job.
COP in Action
Let’s compare a heat pump to an electric baseboard heater. The heater has a COP of 1: all electricity becomes heat. A typical heat pump has a COP of around 2.5. This means the heat pump gives you 2.5 times more heat than the baseboard heater using the same electricity! That translates into major savings on your heating bills.
COP for Environmental Impact
COP isn’t just about money. A higher COP means your heat pump uses less electricity. That reduces your carbon footprint and helps fight climate change. COP is a key reason why heat pumps are a preferred choice for decision-makers and anyone concerned about the environment.
Factors Affecting cop heat pump
Several factors influence the COP of a heat pump system: Ambient temperature: When the temperature difference between the heat source (for example outside air, ground or water) and the desired interior temperature increases, the COP decreases. This is because the heat pump has to work harder to transfer heat across higher temperature gradients. System design: The design and components of the heat pump system can have an impact on its COP. Modern, well-designed systems tend to have higher COP values due to improved technology and engineering. Refrigerant Type: The choice of refrigerant can significantly affect the COP. Low GWP (global warming potential) refrigerants are generally more environmentally friendly and can lead to higher COP values. Maintenance: Regular maintenance and cleaning of heat pump components can help maintain or improve COP over time. Dirty coils or filters can reduce efficiency. Operating Conditions: COP may vary depending on different operating conditions, such as load demand, humidity levels and system capacity.
Conclusion
The coefficient of performance (COP) shows the efficiency of heat pump systems. It quantifies how efficiently these systems transfer heat, making it an essential tool for individuals, businesses and policymakers striving to achieve greater energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact . By understanding and optimizing COP rating, we can make significant progress towards a sustainable and energy-efficient future.
1 Comment
Adam Wilson
October 3, 2023dfgdgdgb